Table Of Content
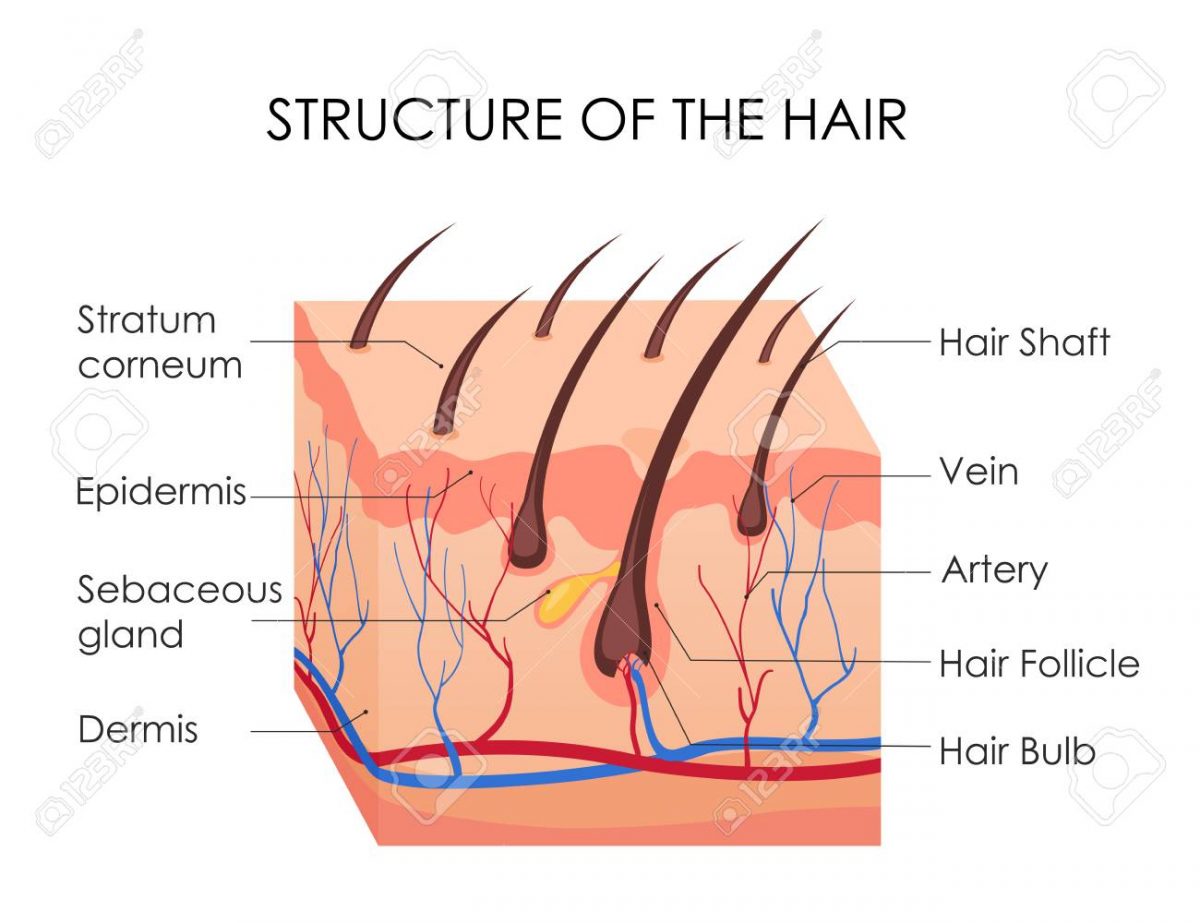
The isthmus is the area between the sebaceous duct opening and the bulge. The bulge is an area of the follicle marked by the insertion of the arrector pili muscle. Also, the bulge contains several epidermal stem cells that are part of the outer root sheath and stain with CK19, CK15, and CD200.
‘Grey’s Anatomy’ Star Jesse Williams Debuts New Blue Hair Makeover — Before & After Pics - HollywoodLife
‘Grey’s Anatomy’ Star Jesse Williams Debuts New Blue Hair Makeover — Before & After Pics.
Posted: Tue, 28 Jul 2020 07:00:00 GMT [source]
1. Hair growth cycle
When the muscle contracts, it causes the hair to stand up, otherwise known as goosebumps. Season 19 saw the introduction of five new interns with Simone Griffith, Mika Yasuda, Benson Kwan, Jules Millin and Lucas Adams, the latter of which is revealed to be a nephew of Amelia and Derek Shepherd. Meredith Grey, one of the last remaining original characters of the series, as well as Pierce, both depart Seattle during the course of the nineteenth season. Grey's Anatomy has been well received by critics throughout much of its run and has been included in various critics' year-end top 10 lists.
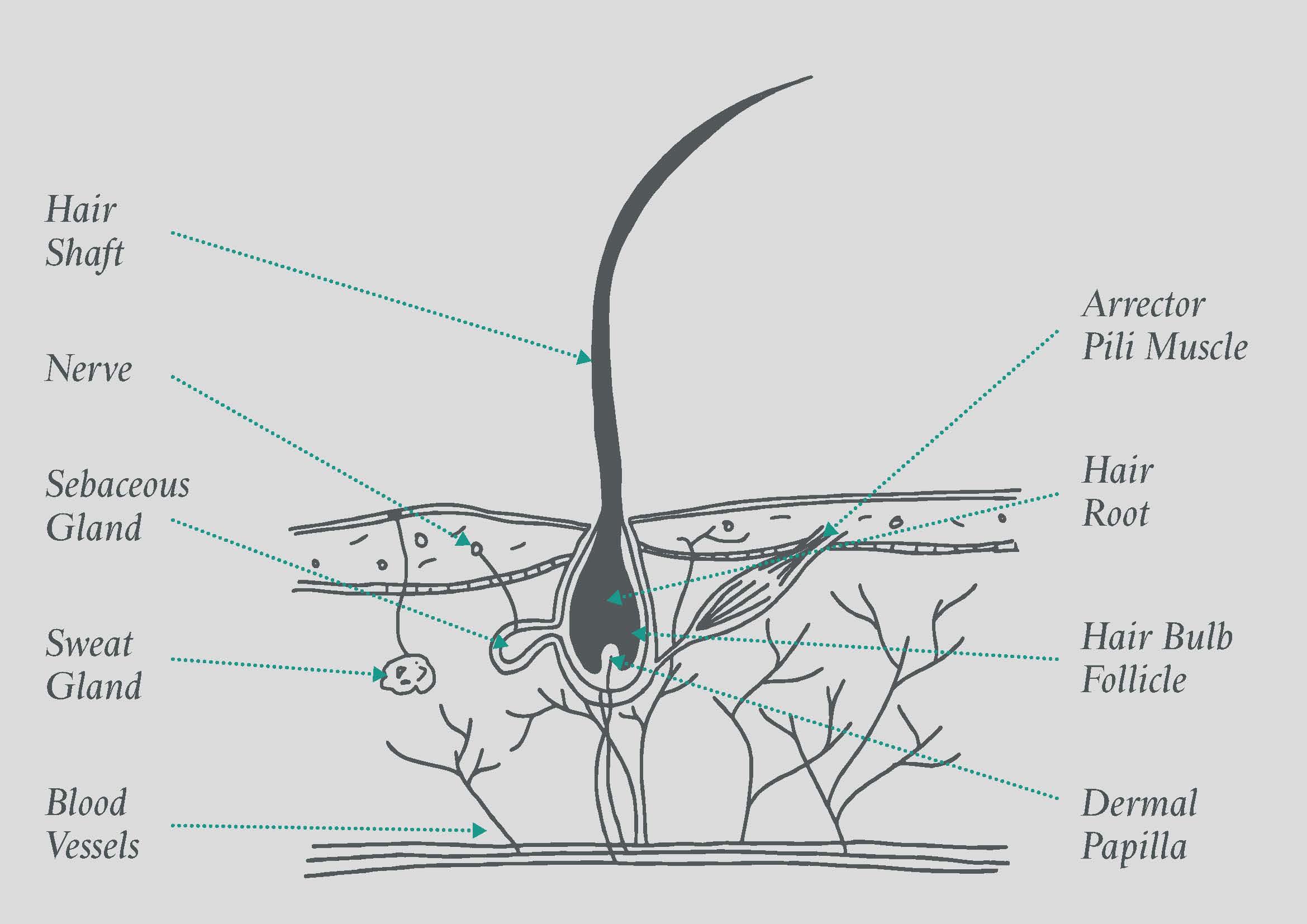
2. Structure of the hair
While creating characters, as well as writing the first script, the series' writers had no character descriptions in mind, and hoped to cast the best actor available for each part. Rhimes has said that if the network had not allowed her to create characters this way, she would have been hesitant about moving forward with the series.[115] Female roles, in particular, were developed as multi-faceted characters. The series also shows drama and emotions focused on Meredith's life.
General structural features from the X-ray experiments
During the growth phase, an extra outer layer (stratum basale) appears. Androgenetic alopecia, which is known as male pattern baldness when it presents in men, is a condition that affects the growth cycle of hair follicles on the scalp. The hair cycle slows down and weakens, eventually stopping altogether. Hair serves a variety of functions, including protection, sensory input, thermoregulation, and communication. The hair in the nose and ears, and around the eyes (eyelashes) defends the body by trapping and excluding dust particles that may contain allergens and microbes.
The resulting 2-dimensional X-ray intensity maps of the reciprocal space reveal exquisite details of the molecular structure of human scalp hair, as presented in Fig. The displayed (qz, q‖)-range was determined to cover the length scales of the features of interest in preliminary experiments. The individuals include men and women and hair of different appearance, such as thickness, colour and waviness, and also genetically related hair samples from a father and daughter, a pair of identical and a pair of fraternal twins. The cuticle is the outermost layer formed by flat overlapping cells in a scale-like formation (Robbins, 2012). These cells are approximately 0.5 µm thick, 45–60 µm long and found at 6–7 µm intervals (Robbins, 2012). The outermost layer of the cuticle, the epicuticle, is a lipo-protein membrane that is estimated to be 10–14 nm thick (Swift & Smith, 2001).
It is interesting to note that differences are observed for the fraternal twins in Fig. This finding is in agreement with the expectation that individuals with similar genetics would share similar physical traits such as hair structure. Identical or monozygotic twins originate from one zygote during embryonic development, and they share 100% of their genetic material. Fraternal or dizygotic twins develop from the fertilization of two different eggs and they only share 50% of their DNA on average (Nussbaum et al., 2007). In particular, Subject 1 and 2 are daughter and father, Subjects 10 and 11 are fraternal twins, and Subjects 9 and 12 are identical twins. While in general, the diffraction patterns in the membrane region were found to be different (as demonstrated in Fig. 7A), the genetically similar hair of father and daughter and identical twins show identical patterns within the resolution of our experiment.
Root of the hair
Telogen effluvium describes a disruption in the normal hair growth and rest cycles that results in excessive shedding and hair loss. This disorder is diagnosed by the hair pull test, which is positive when pulled hair easily is removed from the scalp, and 50% or more of the strands are in the telogen, or inactive, phase. This condition can be precipitated by physical stress, such as surgery or malnutrition, or by medical exposure, such as chemotherapy and common medications. Arrector pili muscles are a type of smooth muscle found at an angle to hair follicles. They are attached to the papillary layer of the scalp’s dermis and connective tissue.
Hair growth cycle
The exact mechanism that controls passage from one phase into the next is not fully known. The outer root sheath (ORS) has been recognized as a ready supply of multipotent stem cells that differentiate into several cell types, including melanocytes and keratinocytes. More specifically, these stem cells are thought to reside in a distinct bulge area located between the insertion of the arrector pili muscle and the ductal opening of the sebaceous gland. Once the hair follicle has developed in the fetus, lanugo hairs grow in utero.
5. Immunology of hair follicle
Take your career to the next level.Start your journey to becoming alicensed cosmetologist with CobaAcademy. Learn classic hairstylingtechniques to the latest balayage trends.Click here to learn more. Hair follicles originate in the epidermis and have many different parts. The innermost layer (medulla) is frequently difficult to visualize. Routine light microscopy is typically used to visualize this layer, because the layer is discontinuous in many cases and is often completely absent.
The matrix is the part of the hair follicle where matrix keratinocytes proliferate to form the hair shaft of growing hair. Melanocytes are mixed amongst the matrix cells to provide the hair shaft with color. The isthmus is the lower portion of the upper part of hair follicle between the opening of the sebaceous gland and the insertion of arrector pili muscle. At the isthmus level, epithelium keratinization begins with the lack of granular layer named “trichilemmal keratinization” [14, 16]. Only few differentiated corneocytes remain and the invagination of the epidermis in this area must be considered as highly permeable for topically applied compounds [19]. Hair follicle stem cells are thought to reside in the bulge area on the isthmus close to the insertion of the arrector muscle [20].
The qz intensity was integrated azimuthally for an angle of 25 degrees over the meridian. The q‖ intensity was integrated azimuthally for an angle of 25 degrees over the equator, as depicted in Fig. The aim of this chapter is to enhance the knowledge of the complex anatomy and physiology of the hair in a simple manner (Table 1) [2, 5].
In humans, hair has various functions such as protection against external factors, sebum, apocrine sweat and pheromones production and thermoregulation. The hair also plays important roles for the individual’s social and sexual interaction [1, 2]. Also referred to as the superficial fascia, the connective tissue of the scalp is a fibrofatty layer. This layer forms the bridge between the skin and the epicranial aponeurosis by connecting the two together. The tissue is also innervated with blood vessels and nerve endings. The fact that the blood vessels are attached to the connective tissue is limiting to survival.
Hair care routines differ according to an individual's culture and the physical characteristics of one's hair. Hair may be colored, trimmed, shaved, plucked, or otherwise removed with treatments such as waxing, sugaring, and threading. Many mammals have fur and other hairs that serve different functions. Hair also has a sensory function, extending the sense of touch beyond the surface of the skin. Guard hairs give warnings that may trigger a recoiling reaction.
The corresponding signals are observed in the 2-dimensional data in Fig. The exact position of the features is, however, best determined in small angle diffraction experiments (SAXS), which offer a drastically improved resolution, and will be shown below. We note that the axial packing of coiled-coils within keratin filaments in hair gives rise to a number of fine arcs along the meridian (z).
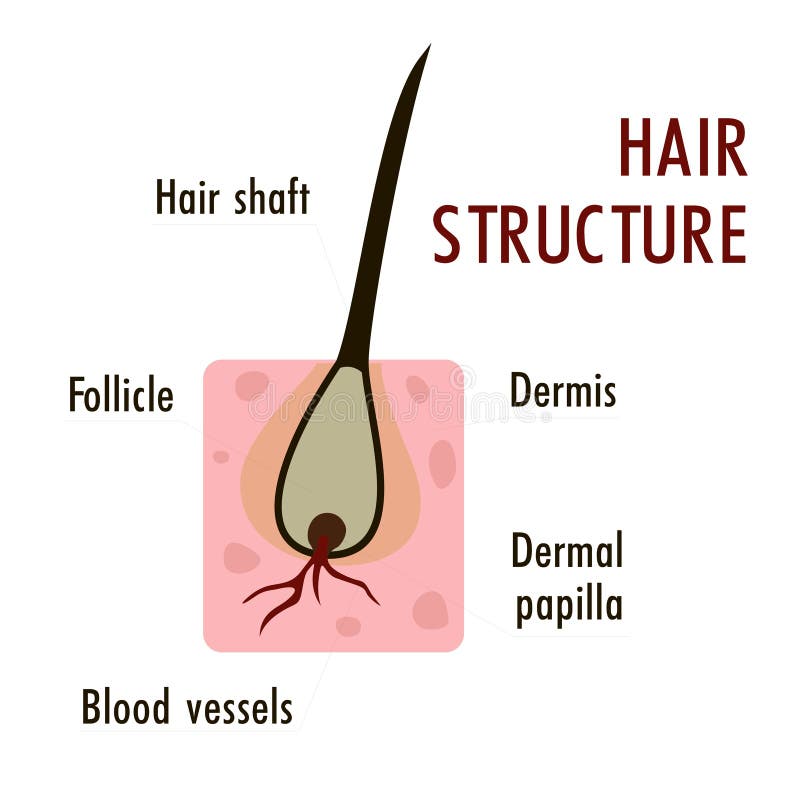
In some follicles, there is a distinct single cell layer interposed between the outer and inner root sheaths, known as the companion layer [23]. The ORS of the hair follicle also contains melanocytes, Langerhans cells and Merkel cells. These cells take place in certain functions of the follicle such as acting as a sensory organ and serving as an immunologic sentinel for the skin [5]. When a hair is actually growing, epithelial cells around the dermal papilla multiply. There is another outer layer, and this is known as the stratum basale of the scalp’s epithelial surface. The mass of epithelial cells found around the dermal papilla whilst the hair is growing is known as the hair root.
White or gray hair is a sign of age or genetics, which may be concealed with hair dye (not easily for some), although many prefer to assume it (especially if it is a poliosis characteristic of the person since childhood). Although pattern baldness can be slowed down by drugs such as Finasteride and Minoxidil or treated with hair transplants, many men see this as unnecessary effort for the sake of vanity and instead shave their heads. In early modern China, the queue was a male hairstyle in which the hair at the front and top was shaved every 10 days in a style mimicking pattern baldness, while the remaining hair at the back was braided into a long pigtail. Hair has its origins in the common ancestor of mammals, the synapsids, about 300 million years ago. It is currently unknown at what stage the synapsids acquired mammalian characteristics such as body hair and mammary glands, as the fossils only rarely provide direct evidence for soft tissues. Your hair growth rate can be affected by your age, hair type, and your overall health.

No comments:
Post a Comment